CSEC Physics Syllabus - Effective for examinations from May - June 2015
Section A - Mechanics
Statics
Forces
Forces
Specific Objective 3.1
explain the effects of forces;
Specific Objective 3.2
identify types of forces;
Specific Objective 3.3
determine the weight of objects.
 |
| Pixabay |
What is a Force?
A force is a push or a pull.
What are the Effects of Forces?
A force may be used to change the shape of, speed up, slow down and/or change the direction of an object.Types of Forces
Forces can be categorized into two groups: Contact and Non-contact forces.
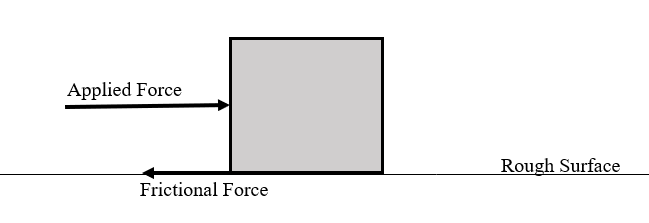
Contact Forces
Applied Force (Thrust)
Frictional Force (Friction)
Tensional Force (Tension)
A force transmitted through a string, rope or wire which is pulled tort by forces acting from each end.
 |
| Tension is created when a rope attached to a vertical wall is pulled by an Applied Force. |
Spring Force
The force exerted by a stretched or compressed spring on an object.
Normal Force (Normal Reaction)
Non-Contact Forces
Electric Forces
This is a force of attraction that exists between positive and negative electric charges and a force of repulsion that exists between two or more positive or negative electric charges. This force also exists between electric fields and electric fields and electric charges.
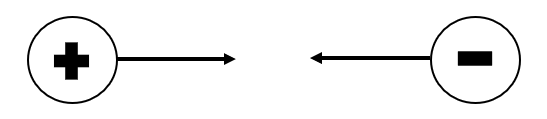 |
| Opposite charges attract each other. |
 |
| Like charges repel each other. |
Magnetic Forces
This is the force of attraction that exists between a north and a south pole and a force of repulsion between two north or south poles of a magnet. This force also exists between magnets and current carrying conductors.
 |
| Unlike poles attract each other. |
 |
| Like poles repel each other. |
Nuclear Forces
These are very strong forces that hold particles together in the nucleus of the atom.
 |
| The nucleus of the Atom. |
Gravitational Force (Gravity)
This is the force of attraction between two or more masses. They are weak but may be sizeable if one of the masses as large as a planet.
Gravity on the Earth = 9.81 N/kg
Gravity on the Moon = 1.62 N/kg
Gravity on the Moon = 1.62 N/kg
Finding the Weight of Objects
Definition of Weight:
Weight is an applied force an object applies to a surface due to gravity. The weight of an object varies from planet to planet and with latitude on a given planet. The vector representing the weight of an object is drawn from the center of mass of the object and points vertically downwards.Symbol:
Weight, W.Unit:
Newton, N.Formula:
Weight = Mass × Gravity
W = m × g
Example 1
Steve measured his mass using a bathroom scale and read 75 kg. What is his weight on Earth and on the Moon, if the gravity on the Earth is 9.81 N/kg and 1.62 N/kg on the Moon.Example 2
The Samsung Galaxy S10 has a mass of 157 g. Determine its weight on Earth and on the Moon.









0 Comments